Read the full article in the following link: https://zenodo.org/records/14040638
Enebral-Romero Estefanía, García-Fernandez Daniel, Gutierrez-Galvez Laura,
Lopez-Diego David, Luna Monica, García-Martín Adrian, Salagre Elena, Michel Enrique G., Torres Inigo, Zamora Felix, García-Mendiola Tania, Lorenzo Encarnacion
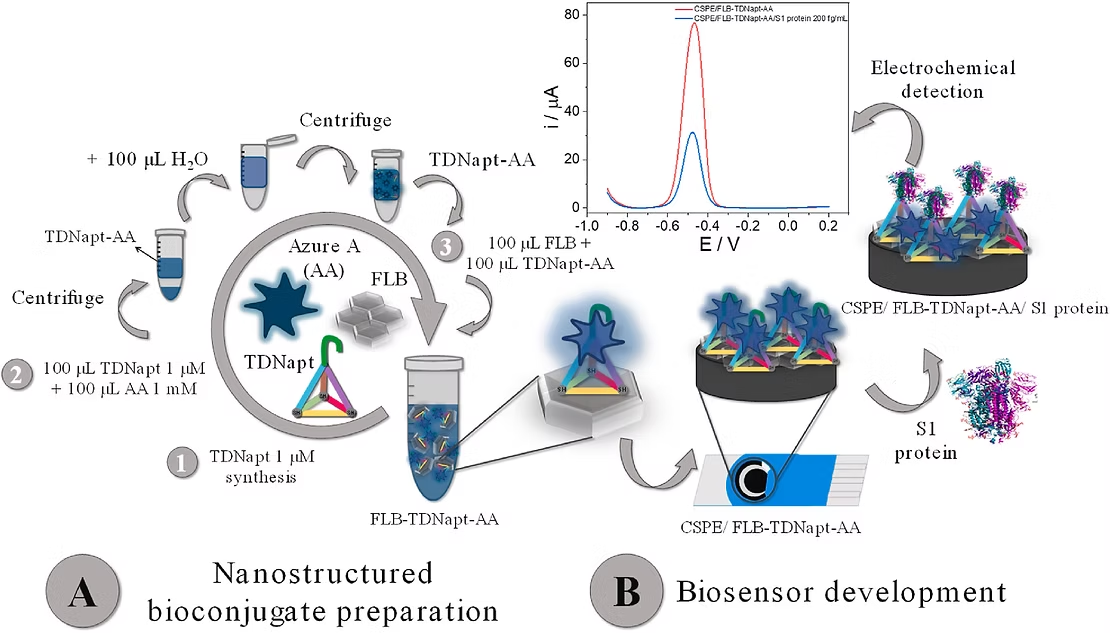
In this work, we present an electrochemical sensor for fast, low-cost, and easy detection of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in infected patients. The sensor is based on a selected combination of nanomaterials with a specific purpose. A bioconjugate formed by Few-layer bismuthene nanosheets (FLB) and tetrahedral DNA nanostructures (TDNs) is immobilized on Carbon Screen-Printed Electrodes (CSPE). The TDNs contain on the top vertex an aptamer that specifically binds to the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, and a thiol group at the three basal vertices to anchor to the FLB. The TDNs are also marked with a redox indicator, Azure A (AA), which allows the direct detection of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein through changes in the current intensity of its electrolysis before and after the biorecognition reaction. The developed sensor can detect SARS-CoV-2 spike protein with a detection limit of 1.74 fg mL 1 directly in nasopharyngeal swab human samples. Therefore, this study offers a new strategy for rapid virus detection since it is versatile enough for different viruses and pathogens.